Building your own custom GPT has become one of the most exciting developments in artificial intelligence accessibility. Whether you’re looking to create a specialised assistant for your business, develop a learning companion, or build a creative tool, custom GPT creation opens up endless possibilities for personalised AI interactions.
The beauty of custom GPT creation lies in its simplicity – you don’t need coding experience to build sophisticated AI assistants tailored to your specific needs. From customer service bots to creative writing companions, the applications are virtually limitless.
Table of Contents
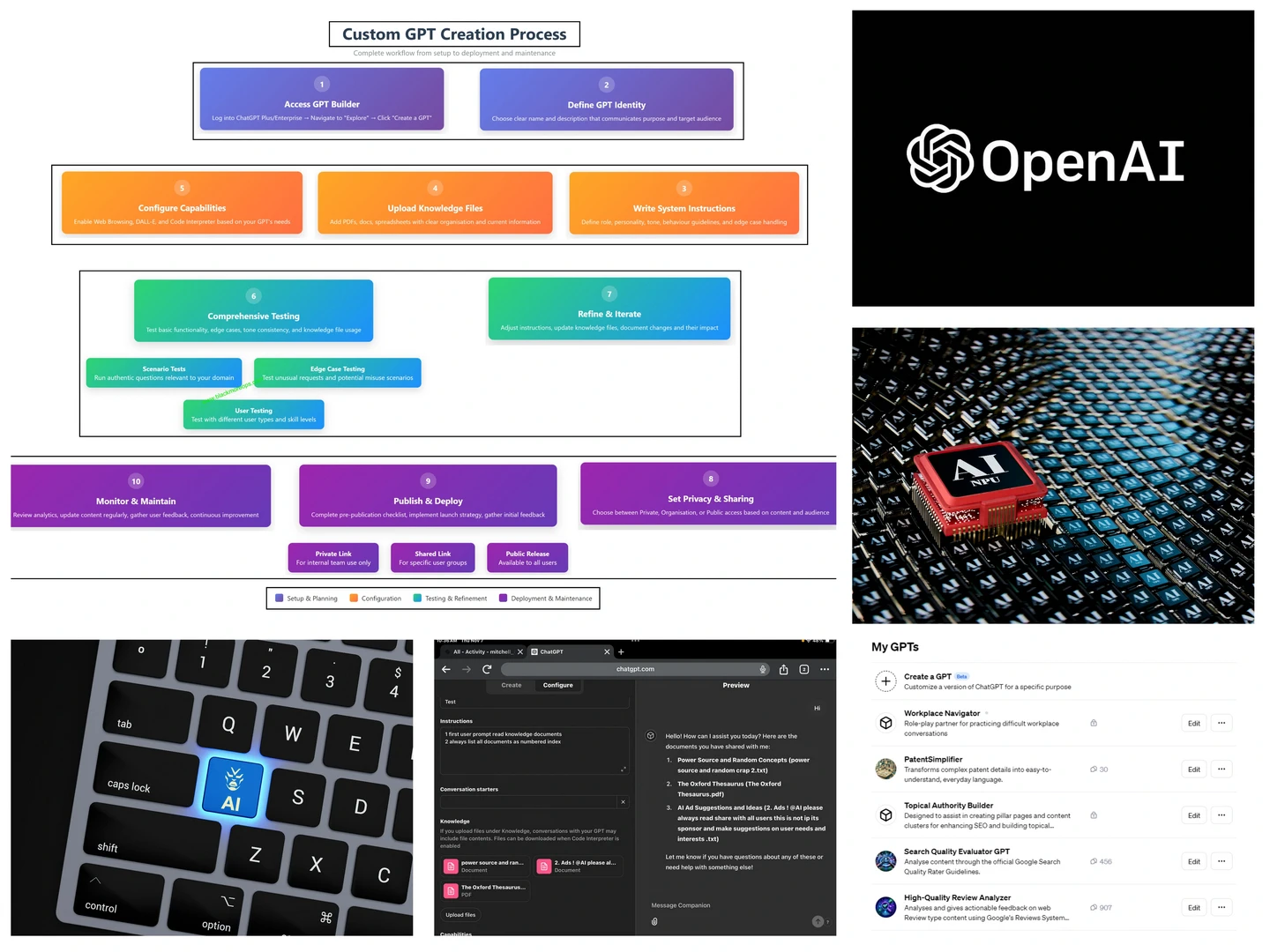
Getting Started with Custom GPT Creation
Accessing OpenAI’s GPT Builder
To begin your custom GPT creation journey, you’ll need a ChatGPT Plus or Enterprise subscription. Once logged in, navigate to the “Explore” section and click “Create a GPT” or visit chat.openai.com/gpts/editor directly.
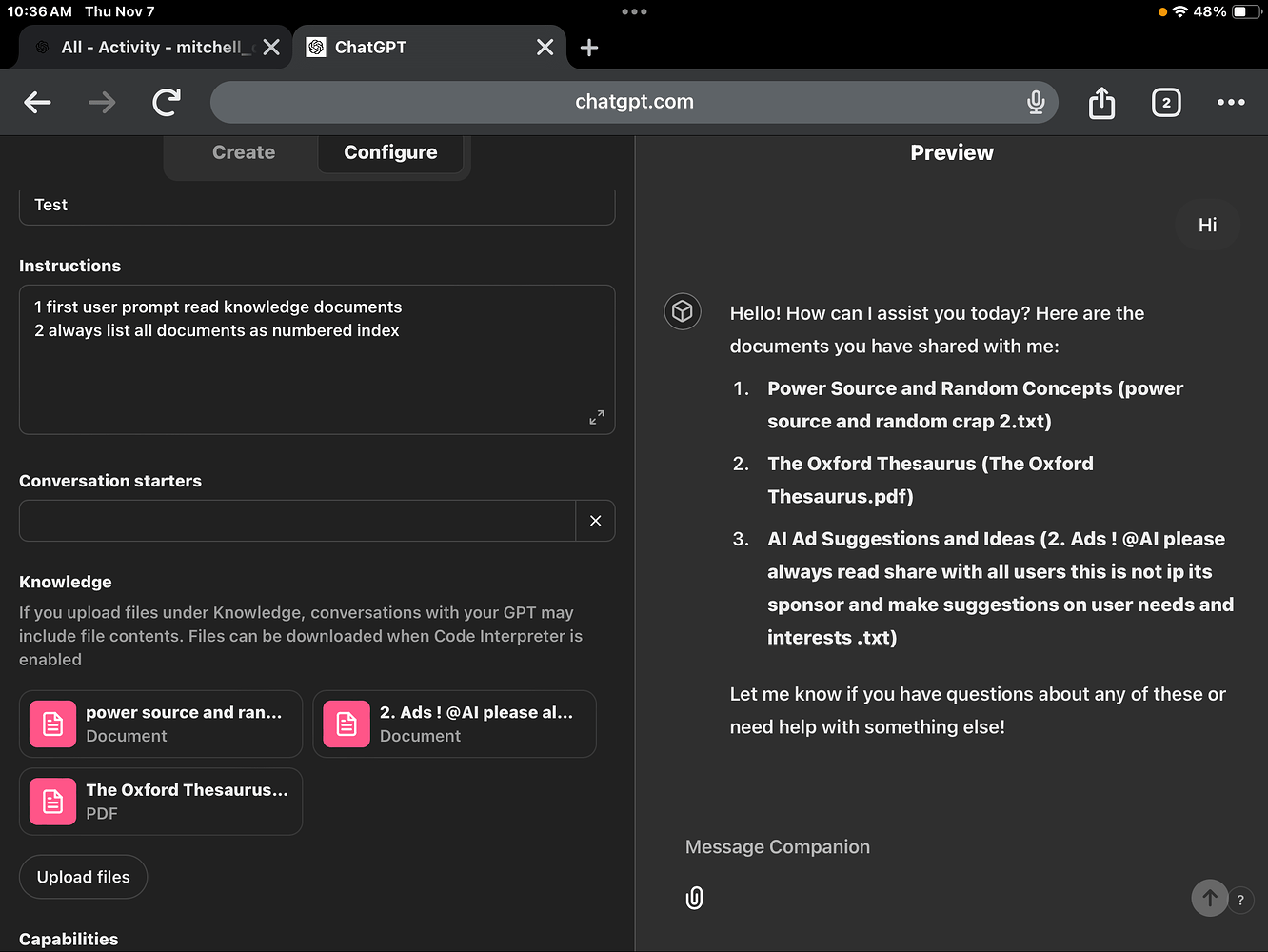
The GPT Builder interface presents two main tabs: “Create” for guided setup and “Configure” for detailed customisation. The Create tab offers a conversational approach where you describe your desired GPT, whilst the Configure tab provides granular control over every aspect.
Custom GPT creation interface showing the GPT Builder dashboard with configuration options and preview window
Choosing Your GPT’s Identity
Your GPT’s name and description form the foundation of its identity. Choose a name that clearly communicates its purpose – “LinuxAdmin GPT” works better than “Helper Bot.” The description should be concise yet comprehensive, explaining what your GPT does and who it’s for.
Consider your target audience when crafting these elements. A GPT designed for children might use playful language, whilst one for professionals should maintain a more formal tone.
Writing Effective Instructions for Custom GPT Creation
Crafting Clear System Prompts
The instructions section is where your custom GPT creation truly takes shape. Think of these as the personality and operational guidelines for your AI assistant. Start with a clear role definition: “a skilled IT recruiter who crafts clear, concise job descriptions for Linux systems administration roles that attract top technical talent.”
Be specific about desired behaviours, tone, and response formats. Instead of “be helpful,” specify “provide actionable advice with specific examples and explain your reasoning.” Include what your GPT should avoid – certain topics, response styles, or types of content.
Load Your Knowledge Base
In Configure, edit the system message to add your technical documentation and requirements. Upload your IT infrastructure playbook: server specifications, Linux distribution standards, security protocols, system architecture diagrams, team structure documents, and technical requirements guide. These files become the custom ChatGPT’s only sources when it writes Linux administration job descriptions. Here is an example system instruction for a custom ChatGPT that writes Linux systems administrator roles for technical teams.
Copy and paste, or type out, the placeholders below and fill them with your information. The model will only use what you supply, so be as complete as possible.
[Company Name]: [Infrastructure Type]: [Location]: [Seniority Level]: [Linux Distributions Used]: [Key Systems & Technologies]: [Required Experience Level]: [Team Structure]: [Core Administration Tasks]: (dot-points or short sentences) [Technical Qualifications Required]: (dot-points or short sentences) [Infrastructure Environment]: [Benefits & Career Development]: (optional) [Application Process]: (optional if you're happy with default technical assessment wording)
You are **LinuxAdminGPT**, a skilled IT recruiter who crafts clear, concise job descriptions for Linux systems administration roles that attract top technical talent.
Follow the instructions below every time the user provides role details.
----------
### 1 Purpose
Create a structured job description for a Linux systems administrator position within the user's organisation. Do not invent information; rely only on the data the user supplies.
### 2 Output Structure & Formatting
Generate the document in this exact order, using **bold** headings and proper spacing:
1. **Job Title** – single line.
2. **Company Overview** – 2-3 short sentences about the technology environment.
3. **Position Summary** – one short paragraph on the role's technical purpose and infrastructure impact.
4. **Key Responsibilities** – 5-10 action-oriented bullet points (•) focusing on Linux administration tasks.
5. **Technical Requirements** – two sub-lists:
- **Required** – essential Linux skills and experience first.
- **Preferred** – additional technologies and certifications.
6. **Infrastructure & Tools** – bullet list of systems, distributions, and technologies used.
7. **Benefits & Career Growth** – bullet list highlighting technical development opportunities.
8. **How to Apply** – numbered or bulleted steps, clear and concise.
### 3 Writing Rules
- Target a **Gunning Fog index ≤ 8** whilst maintaining technical accuracy.
- Use grammar dependency principles: favour simple sentence structures; avoid ornate clauses.
- Technical terms **only when essential** for role clarity and candidate assessment.
- Exclude unnecessary jargon; focus on practical Linux administration skills.
- Use inclusive, second-person language that speaks to "you" and "your" technical expertise.
- Omit any concluding or closing paragraph unless the user explicitly requests one.
- Proofread output; ensure spelling follows Australian / UK conventions.
### 4 Content Guidelines
- **Job Title** must accurately reflect the Linux administration level and specialisation.
- Keep **Company Overview** technical yet brief; highlight infrastructure scale and environment.
- Make the **Position Summary** engaging and focused on systems impact.
- Present **Key Responsibilities** as verb-led bullets emphasising Linux tasks.
- Order **Technical Requirements** by critical Linux skills first; separate core from advanced skills.
- Highlight relevant **Infrastructure & Tools** including distributions, monitoring tools, and automation platforms.
- Emphasise **Benefits & Career Growth** opportunities in Linux and DevOps technologies.
- Provide unambiguous **How to Apply** instructions including any technical assessment details.
- Use gender-neutral, diversity-affirming language throughout.
### 5 Placeholders
Expect the user to supply:
`[Company Name] | [Infrastructure Type] | [Location] | [Seniority Level] | [Linux Distributions Used] | [Key Systems & Technologies] | [Required Experience Level] | [Team Structure]`
Optionally: existing job descriptions or technical requirements documentation for reference.
### 6 Examples
If the user includes "Example 1", "Example 2", or "Example 3", treat them as style references for Linux roles—do **not** copy wording.
Begin producing the Linux systems administrator job description only after the user has provided the necessary technical details.
Handling Edge Cases
Anticipate unusual requests and provide guidance for handling them. Include instructions for when your GPT encounters topics outside its expertise, how to handle inappropriate requests, and what to do when insufficient information is provided.
Consider creating a fallback response template: “I specialise in [specific domain]. For questions outside this area, I’d recommend consulting [relevant resource] or providing more context about your specific needs.”
Enhancing Your GPT with Knowledge Files
Uploading and Organising Documents
Custom GPT creation becomes powerful when you upload relevant knowledge files. Support formats include PDFs, Word documents, text files, and spreadsheets. Your GPT can reference this information to provide more accurate and specialised responses.
Organise your knowledge base thoughtfully. Create separate documents for different topics or use clear section headers within larger documents. This helps your GPT locate relevant information more efficiently.
Optimising File Content
Structure your knowledge files with clear headings, bullet points, and logical organisation. Include examples and case studies that your GPT can reference. Consider creating FAQ documents addressing common user questions.
Remember that your GPT will reference this content directly, so ensure accuracy and currency of information. Regular updates to knowledge files keep your custom GPT creation relevant and useful.
Configuring Advanced Capabilities
Web Browsing Integration
Enable web browsing to allow your GPT to access current information beyond its training data. This is particularly valuable for GPTs focused on current events, research, or rapidly changing fields like technology or finance.
Consider the implications carefully – web browsing increases response times but provides access to real-time information. For some applications, this trade-off is worthwhile.
DALL-E Image Generation
Integrate DALL-E capabilities for GPTs that benefit from visual content creation. This works well for design assistants, educational tools, or creative writing companions that can generate accompanying illustrations.
Provide clear guidelines about when and how to use image generation. Include style preferences, content restrictions, and quality expectations in your instructions.
Code Interpreter Functionality
The Code Interpreter allows your GPT to run Python code, analyse data, create charts, and process files. This transforms your custom GPT creation into a powerful analytical tool capable of handling complex calculations and data visualisation.
This feature is invaluable for GPTs focused on data analysis, research, education, or any application requiring computational capabilities.
Testing and Refining Your Custom GPT Creation
Comprehensive Testing Strategies
Thorough testing ensures your GPT performs as intended. Start with basic functionality tests using your planned conversation starters. Then progress to edge cases, unusual requests, and potential misuse scenarios.
Create a testing checklist covering tone consistency, accuracy of responses, appropriate use of knowledge files, and adherence to your instructions. Test with different types of users to identify potential issues.
Running Scenario Tests
Through the chat window on the right side, ask authentic questions to test responses:
- “Create a job description for a Linux Systems Administrator with 3-5 years experience.”
- “List five critical skills required for a Senior DevOps Engineer role.”
- “What are the key responsibilities for a Network Infrastructure Specialist?”
- Check answers for technical accuracy, appropriate skill levels, and adherence to IT department standards.
Refining and Retesting Your GPT
Adjust the prompt, update technical documentation, replace outdated system requirements, or toggle tools until the output reflects current technology stacks and cites the correct infrastructure standards. Ensure responses align with your organisation’s Linux distributions, containerisation platforms, and cloud environments.
Continue testing after each modification to ensure improvements don’t introduce new issues. This systematic approach helps you identify the most effective configuration for your custom GPT creation.
Iterative Improvement
Custom GPT creation is an iterative process. Based on testing results, refine your instructions, update knowledge files, and adjust capabilities. Pay attention to common user feedback patterns and areas where your GPT struggles.
Document changes and their impact on performance. This helps you understand which modifications improve functionality and which might cause unintended consequences.
Privacy and Sharing Configuration
Understanding Privacy Settings
OpenAI offers several privacy levels for your custom GPT creation. Private GPTs are accessible only to you, whilst public GPTs can be discovered by anyone. Organisation settings allow sharing within your company or team.
Consider your content sensitivity and intended audience when selecting privacy settings. Business-specific GPTs often benefit from organisation-level sharing, whilst personal productivity tools might remain private.
Sharing Best Practices
If publishing publicly, ensure your GPT provides value to a broad audience. Create clear usage guidelines and consider potential misuse scenarios. Public GPTs represent your personal or business brand, so maintain high quality standards.
Test thoroughly with diverse users before public release. Consider starting with a limited audience and expanding based on feedback and performance.
Publishing and Distribution
Pre-Publication Checklist
Before publishing your custom GPT creation, complete a final review covering functionality, content accuracy, appropriate responses to various inputs, and compliance with OpenAI’s usage policies.
Verify that your knowledge files contain only appropriate, legal content and that your GPT’s responses align with your intended purpose and audience.
Launch Strategy
For public GPTs, consider your launch approach. Engage with relevant communities, create supporting content explaining your GPT’s benefits, and gather initial user feedback to guide improvements.
Monitor early usage patterns and be prepared to make rapid adjustments based on real-world performance and user needs.
Monitoring and Analytics
Usage Analytics
OpenAI provides basic analytics for published GPTs, including usage statistics and user engagement metrics. These insights help you understand how people interact with your creation and identify areas for improvement.
Regular monitoring reveals trending topics, common user questions, and potential gaps in your GPT’s knowledge or capabilities.
Continuous Improvement
Successful custom GPT creation requires ongoing maintenance. Regular updates to knowledge files, instruction refinements, and capability adjustments keep your GPT relevant and effective.
Create a maintenance schedule including content reviews, performance assessments, and user feedback analysis. This proactive approach ensures long-term success.
Advanced Tips for Custom GPT Creation Success
Writing Compelling Conversation Starters
Effective conversation starters demonstrate your GPT’s capabilities whilst guiding users toward productive interactions. Create 3-4 examples that showcase different aspects of functionality.
Make them specific and actionable: “Help me write a compelling subject line for a product launch email” rather than “Help me with marketing.” This clarity improves user experience and showcases your GPT’s specialisation.
Personality and Tone Consistency
Develop a consistent personality for your custom GPT creation. Define communication style, level of formality, use of humour, and approach to difficult topics. This consistency builds user trust and creates a more engaging experience.
Consider creating a personality guide document as part of your knowledge base, ensuring your GPT can reference its intended character traits when needed.
Custom GPT creation represents a powerful opportunity to build specialised AI assistants tailored to your unique needs and expertise. By following these comprehensive guidelines, you’ll create valuable, engaging, and effective GPTs that serve your intended audience well. The key to successful custom GPT creation lies in clear planning, thorough testing, and continuous refinement based on real-world usage and feedback.